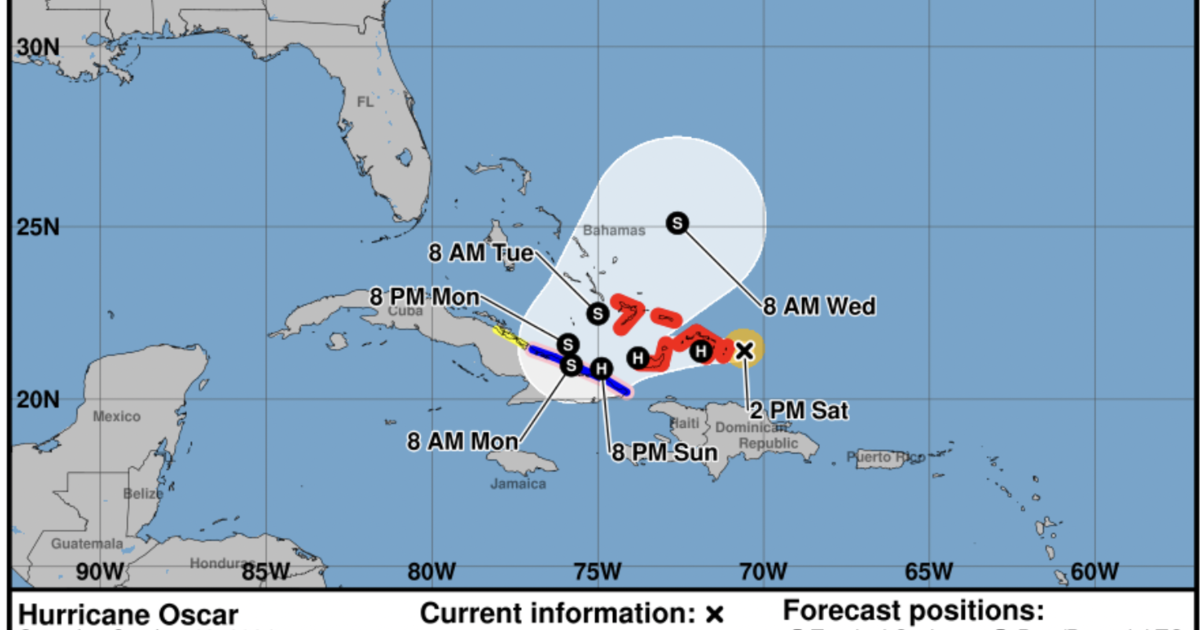
Hurricane Oscar, the fifteenth named storm of the 2024 Atlantic hurricane season, rapidly intensified into a hurricane off the coast of the Bahamas. The National Hurricane Center (NHC) described it as a “tiny” but powerful storm, issuing hurricane warnings for the Turks and Caicos Islands and southeastern Bahamas. Simultaneously, Tropical Storm Nadine impacted Belize and threatened the Yucatan Peninsula, highlighting the unusual and active nature of the season thus far, particularly impacting the already battered Gulf Coast regions of Florida. The rapid intensification of Oscar and the near-simultaneous landfall of Nadine underscore the unpredictable and potentially dangerous nature of the current Atlantic hurricane season, raising concerns about the impact of consecutive storms on vulnerable communities.
Hurricane Oscar’s Formation and Impact
Hurricane Oscar’s rapid development and intensification into a hurricane, mere hours after being classified as a tropical storm, surprised forecasters. Originating east of the Turks and Caicos Islands, the storm quickly gained strength, its maximum sustained winds reaching 80 mph with higher gusts. This rapid intensification is a significant concern, as it leaves less time for communities to prepare and evacuate.
Warnings and Evacuations
The Bahamian government issued a hurricane warning for the Turks and Caicos Islands and southeastern Bahamas, urging residents to take immediate action to protect themselves and their property. Cuba also issued a hurricane watch for several provinces, indicating the potential threat to the island nation. This prompt issuance of warnings highlights the seriousness of the situation and the importance of heeding official advisories during hurricane season. Authorities emphasized the necessity for preparedness and evacuation of vulnerable populations, emphasizing proactive measures and ensuring swift and effective disaster management responses.
Projected Rainfall and Impacts
The NHC warned of heavy rainfall across the Turks and Caicos Islands and southeastern Bahamas, starting late Saturday and into Sunday. Eastern Cuba was also expected to experience significant rainfall, raising concerns about potential flooding and landslides. The storm’s small size made predicting its precise path more challenging, yet emphasizing the potential intensity of impacts, despite its relatively diminutive size in relation to other major hurricanes. These heavy rainfall amounts potentially exacerbate existing issues caused by previous storms in the region and in vulnerable areas which lacked prior infrastructure resilience.
Tropical Storm Nadine’s Landfall in Belize
While Hurricane Oscar gained strength in the Atlantic, Tropical Storm Nadine made landfall near Belize City in Belize, bringing heavy rains and tropical storm-force winds. This simultaneous occurrence of two significant weather systems in close proximity underscores the exceptionally busy hurricane season. The situation is challenging for meteorologists tasked with monitoring and forecasting such concurrent events, demanding constant updates and enhanced predictive capacity.
Warnings and Impacts on the Yucatan Peninsula
A tropical storm warning was in effect for Belize City and the coastal regions of Belize and Mexico’s Yucatan Peninsula, including the popular tourist destination of Cozumel. Heavy rain and tropical storm conditions were reported across Belize and the northern portion of the Yucatan Peninsula, which required significant efforts for search and rescue efforts across both the heavily populated areas and isolated rural areas in need. The proximity of this system to previously impacted zones meant significant emergency resource allocation challenges, particularly with ongoing needs from prior affected locations.
The Busy 2024 Atlantic Hurricane Season
The formation of Hurricanes Oscar and Nadine underscores the unusual activity characterizing the 2024 Atlantic hurricane season. The fact that these two storms formed nearly simultaneously in the Caribbean basin and the Atlantic has added significant concern and impact over resource allocation during the currently active period.
Comparison to Previous Years
The number of named storms surpasses predictions at an unusual pace, compared to the historical average. The impacts on land through rapid intensifications which result in little time to implement precautionary measures means more considerable losses are expected than initially forecasted. The clustering of the storms and frequency of significant hurricanes mean emergency response agencies are currently under stress.
Impact on Florida
Meanwhile in Florida, recovery efforts continued from Hurricane Helene and Hurricane Milton, which hit the Gulf Coast regions less than two weeks apart. This rapid succession of hurricanes severely tested the resources and resilience of coastal communities and placed significant demand on regional and national response capabilities. The repetitive stresses on the impacted regions in short sequence means ongoing impacts that far outlast the initial events themselves, meaning more resources are required to be available across multiple years. The overlapping timeline severely compounds and restricts the ability of aid responses to alleviate the damage caused by the sequential weather events.
Takeaway Points
- Hurricane Oscar rapidly intensified into a hurricane, posing a significant threat to the Bahamas and Cuba.
- Tropical Storm Nadine made landfall in Belize and impacted the Yucatan Peninsula concurrently with Oscar’s approach.
- The 2024 Atlantic hurricane season has been unusually active, surpassing predictions with two significant storms occurring virtually at once.
- Florida’s Gulf Coast communities continue to struggle with recovery efforts from back-to-back hurricanes, Helene and Milton. These overlapping events caused major challenges to relief and recovery.
- The combined occurrence of two powerful hurricanes places exceptional strain on emergency services.